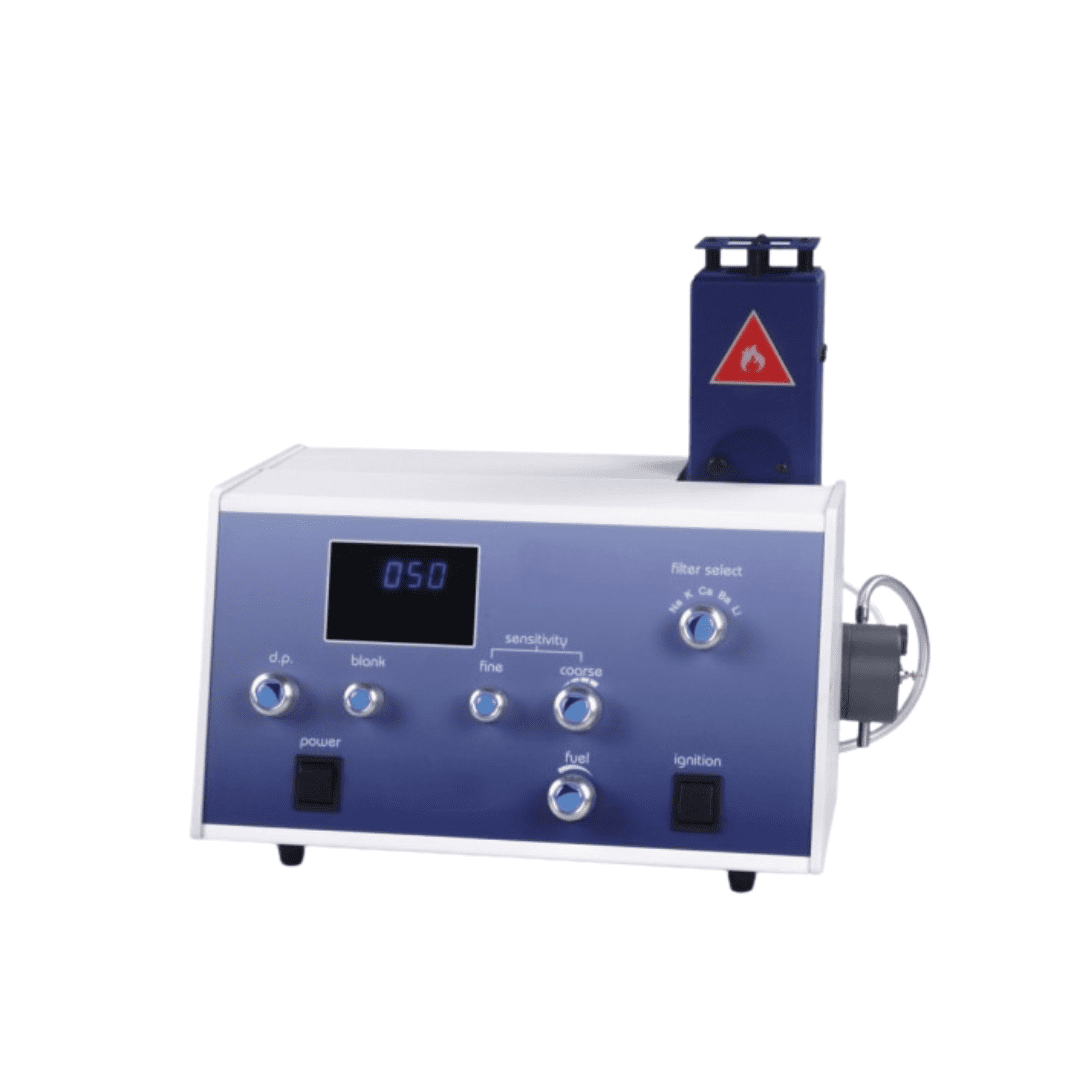
Flame Photometers
Description
Flame Photometers: Essential Tools for Metal Ion Analysis
Flame photometers, also known as flame emission spectrometers, are widely utilized in laboratories for the quantitative determination of alkali and alkaline earth metals. These instruments offer a practical approach to analyzing metal concentrations in various sample matrices.
How Flame Photometers Work:
- Sample Introduction: A liquid sample is aspirated into a flame, where the solvent evaporates, and the sample undergoes atomization.
- Atom Excitation: The high temperature of the flame excites the atoms of the metal ions present in the sample.
- Emission of Light: As excited atoms return to their ground state, they emit light at characteristic wavelengths specific to each element.
- Detection and Measurement: The emitted light passes through optical filters that isolate the wavelengths of interest. A photodetector measures the intensity of the transmitted light, which correlates with the concentration of the specific metal ion in the sample.
Key Applications:
- Clinical Diagnostics: Flame photometers are employed to measure electrolyte levels, such as sodium and potassium, in blood and urine samples, aiding in the diagnosis and management of various medical conditions.
- Environmental Monitoring: These instruments detect trace metals in water and soil, assisting in assessing pollution levels and ensuring compliance with environmental regulations.
- Industrial Quality Control: In industries like food and beverage manufacturing, flame photometers monitor metal ion concentrations to maintain product quality and adhere to safety standards.
Advantages of Flame Photometry:
- Cost-Effective: Flame photometers are generally more affordable than other spectroscopic methods, making them accessible for routine analyses.
- Simplicity and Ease of Use: With straightforward operation and minimal sample preparation, these instruments are user-friendly and require less training.
- Rapid Analysis: Flame photometry provides quick results, suitable for applications requiring timely data.
- Selective Detection: By using specific optical filters, flame photometers can selectively measure particular metal ions, minimizing interference from other elements.
Considerations:
- Elemental Limitation: Flame photometers are primarily suitable for detecting alkali and alkaline earth metals. Elements with low excitation energies are best analyzed using this method.
- Sensitivity: While adequate for many applications, flame photometry may not detect extremely low concentrations of metals. For trace analysis, more sensitive techniques like atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS) might be preferred.
- Calibration and Maintenance: Regular calibration with standard solutions is essential to ensure accurate measurements. Routine maintenance of the instrument is also necessary to uphold performance.
Popular Models:
- Sherwood Scientific Model 410: Renowned for its stable flame design and ease of use, this model is suitable for routine analyses in clinical and industrial settings.
- PG Instruments FP910: A digital, microprocessor-controlled flame photometer capable of measuring sodium, potassium, calcium, barium, and lithium in a single aspiration.
Incorporating flame photometers into laboratory workflows enhances efficiency and reliability in metal ion analysis. Their affordability, ease of use, and rapid results make them invaluable tools across various industries and research fields.